It is no exaggeration to say that 2020 was swayed by COVID-19, and unfortunately it has not gone yet.
The Expat’s Guide to Japan is now sharing information on how to prevent, deal with the viruses and so on with the help of Smart119, a company founded by an active emergency doctors at Chiba University School of Medicine.
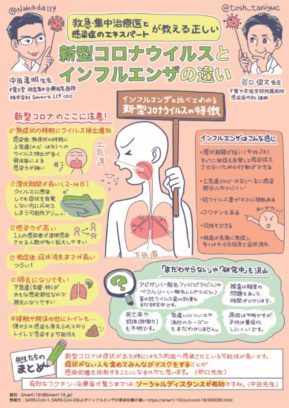
The first topic in the series is “Difference between COVID-19 and influenza”.
Getting a Vaccination
Influenza epidemic begins around the end of summer every year.
When you don’t feel well and think it may be influenza, you may be infected with the COVID-19 that causes more serious symptoms. If you have any similar symptom with the COVID-19 or feel any danger, you need to take the utmost care for yourself and those around you.
* You can get vaccinations for influenza if your wish.
Here is summarize the differences between the COVID-19 and influenza infection.

Covid-19 or Influenza?
・ COVID-19 increases viral shedding during the asymptomatic period (after infection, the viral shedding into the upper respiratory tract, nose/throat, is high during the asymptomatic period, and the infectivity is high due to droplets, etc.)
・ COVID-19 has a long incubation period (2 to 14 days), while Influenza has an average of 2 days so you can immediately become aware of the symptoms and take actions to prevent the spread of the infection.
・ COVID-19 is highly infectious; the number of people directly infected by one infected person is large so it is easier to spread.
・ It takes a long time for the COVID-19 symptoms to disappear after the onset (and it is tough!). On the other hand, symptoms in influenza develops rapidly and disappear in about 4 to 6 days.
・ COVID-19 is prone to pneumonia because the lower respiratory tract, trachea/lungs, is the main infection site, while Influenza mainly infects the upper respiratory tract, throat/nose, so it is less likely to cause pneumonia.
・ COVID-19 infection is considered to be dangerous also in toilets.
・ There are no antiviral drugs or vaccines in COVID-19 yet. It is also unknown if antibodies would be produced. On the other hand, there are multiple antiviral drugs and vaccines for influenza, and antibodies can be produced.
Many things uncertain & under study
・The effects of antiviral drugs such as Avigan
・Mortality rate and antibody (defense)
・The difference in type and the season of epidemic
・Accuracy problems in inspection
・Fact and the reason that children are less likely to become seriously ill
Points of measures
・It is highly possible that the virus has already infected your surroundings when symptoms appear to you.
・Everyone including those who have no symptoms to wear masks will prevent its spread.
・Social distance is also effective until an effective vaccine/therapeutic drug is available.
*The article was written by Professor Takaaki Nakata (Professor of Emergency Intensive Care Medicine, Chiba University) who teaches at Chiba University, and Toshifumi Taniguchi (Lecturer of Internal Medicine, Chiba University Hospital).
The attached manga-style illustration is also supervised by the two above.
*What is Smart119?
Smart119 Co., Ltd. is a venture company established by an active emergency doctor from Chiba University School of Medicine.
More about Smart119.

