 Japan is an island nation located along the east coast of the Asian continent. The Japanese archipelago is composed of four large islands (Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, Kyushu—see below), the islands of Okinawa, and thousands of other smaller islands, with a total land area of
Japan is an island nation located along the east coast of the Asian continent. The Japanese archipelago is composed of four large islands (Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, Kyushu—see below), the islands of Okinawa, and thousands of other smaller islands, with a total land area of  around 364,000 square kilometers—a size comparable to California or Germany. The islands stretch from the sub-arctic Hokkaido (geographical latitude comparable to Toronto or Milan) to subtropical Okinawa (comparable to the Bahamas). Japan’s closest neighbors are Korea, China, and Russia.
around 364,000 square kilometers—a size comparable to California or Germany. The islands stretch from the sub-arctic Hokkaido (geographical latitude comparable to Toronto or Milan) to subtropical Okinawa (comparable to the Bahamas). Japan’s closest neighbors are Korea, China, and Russia.
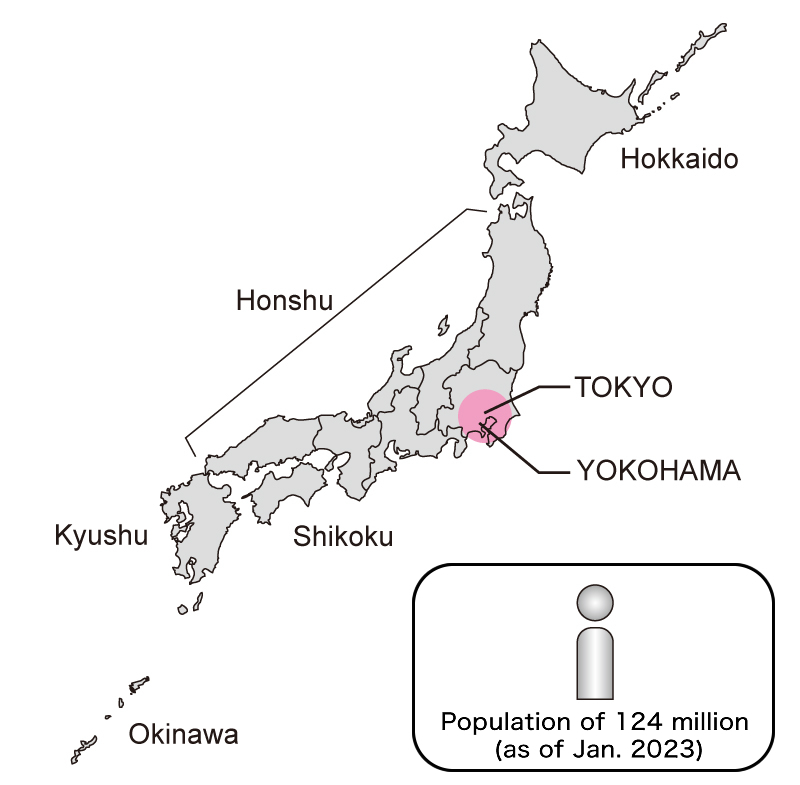
Japan has a population of around 124 million, making it the 10th most populous nation in the world. Roughly 70% of the landmass is mountainous, and population centers developed around the remaining 30%. 75% of the population live in urban areas, resulting in a high urban population density.
Despite crowding, over half of Japan is unpopulated, with over half of the nation’s land consisting of steep, forest-covered mountains and volcanic zones. Japan’s location above several fault systems results in frequent seismic occurrences each year.
The nation is traditionally divided into 8 regions (Hokkaido, Tohoku, Kanto, Chubu, Kinki/Kansai, Chugoku, Shikoku, and Kyushu), which are further divided into 47 prefectures for governmental administration. Tokyo, the capital city, is located in the Kanto region on the main island of Honshu.
